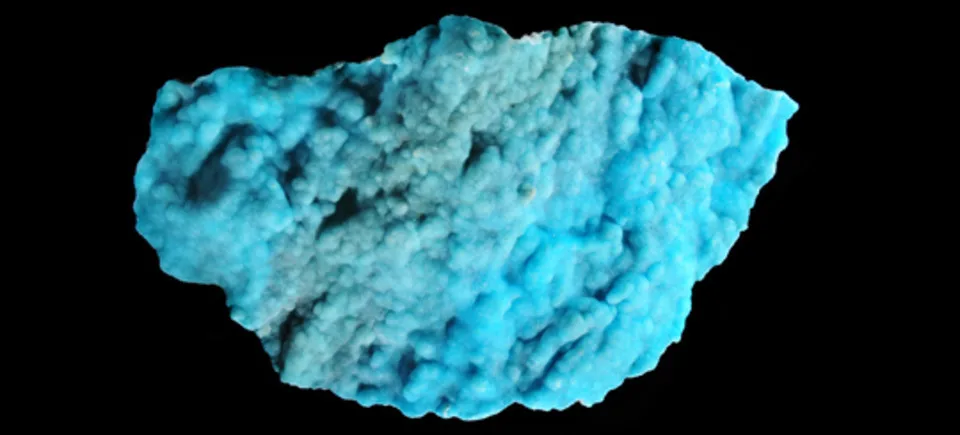
Hemimorphite
Hemimorphite is a sorosilicate mineral which has been mined from days of old from the upper parts of zinc and lead ores, chiefly associated with smithsonite. It was often assumed to be the same mineral and both were classed under the same name of calamine. In the second half of the 18th century it was discovered that there were two different minerals under the heading of calamine – a zinc carbonate and a zinc silicate, which often closely resembled each other.
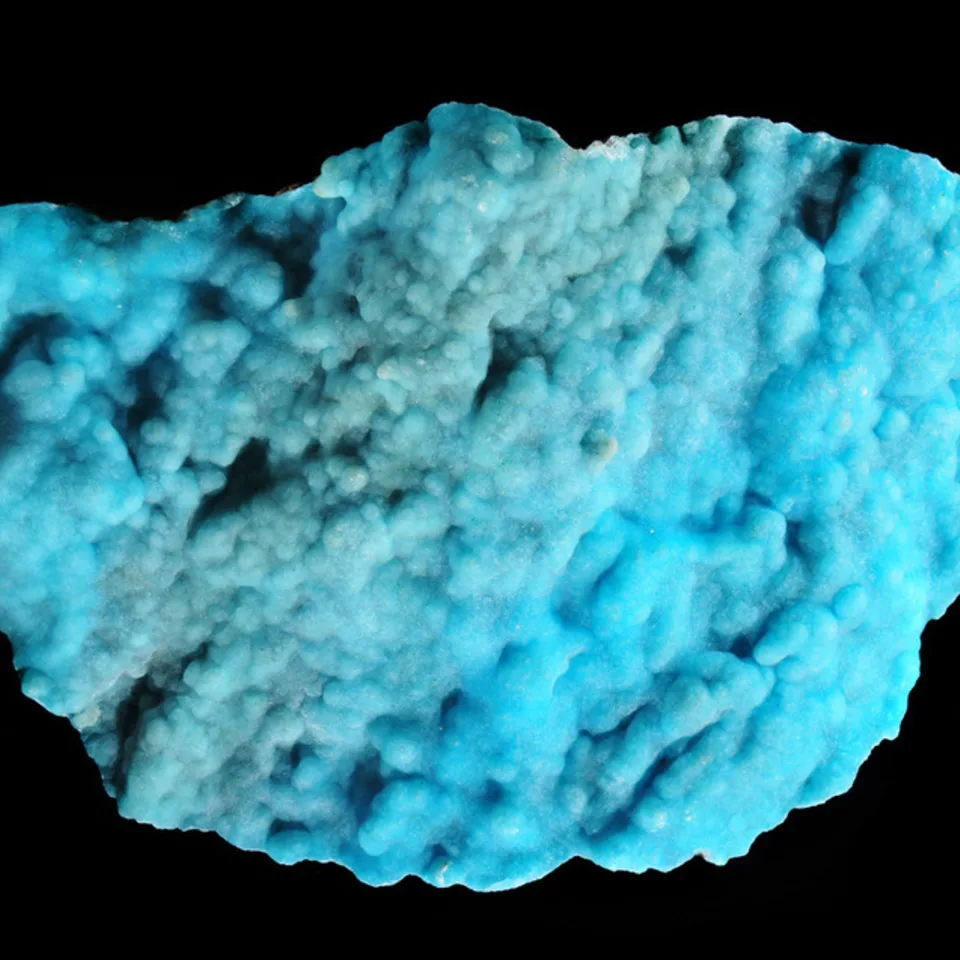
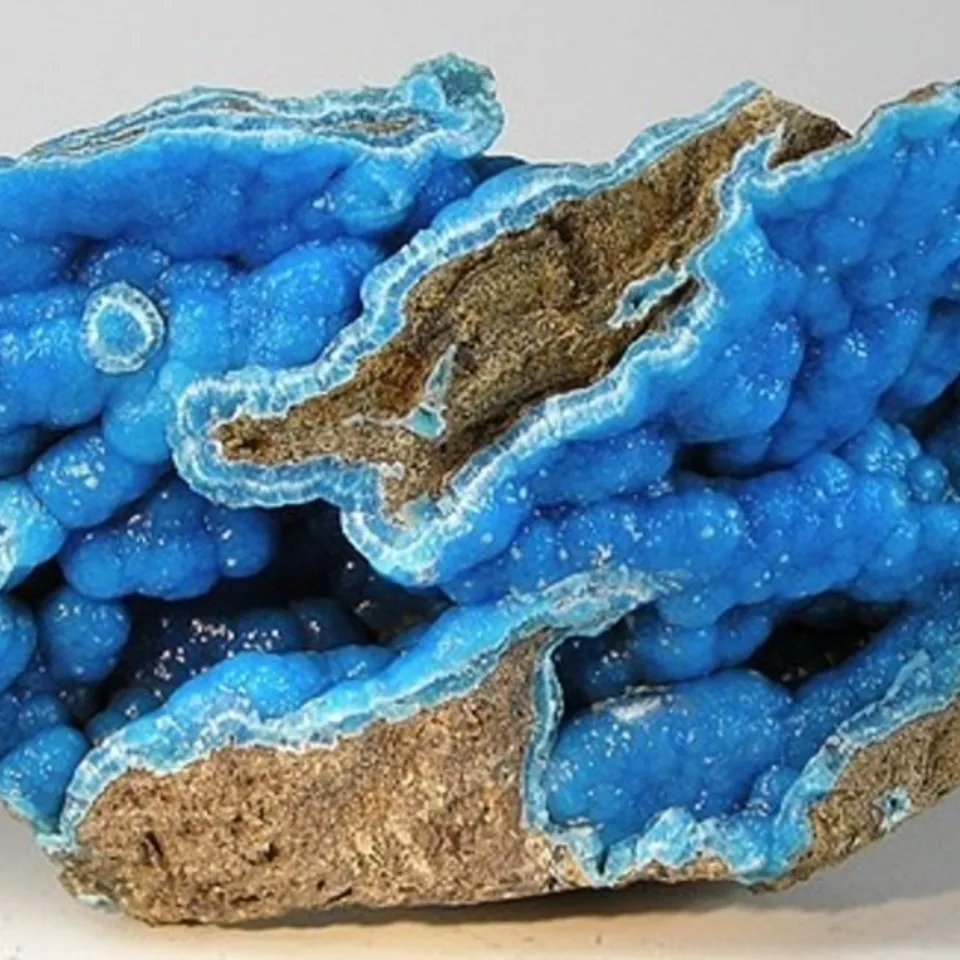
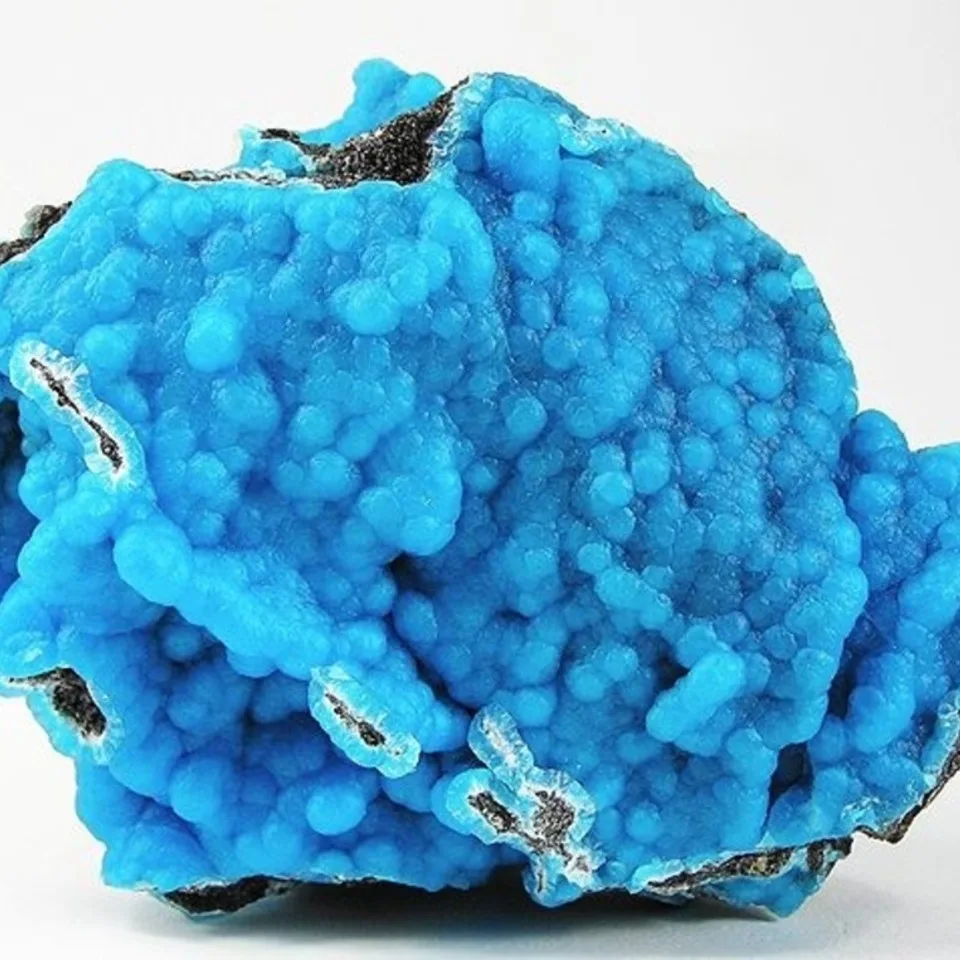
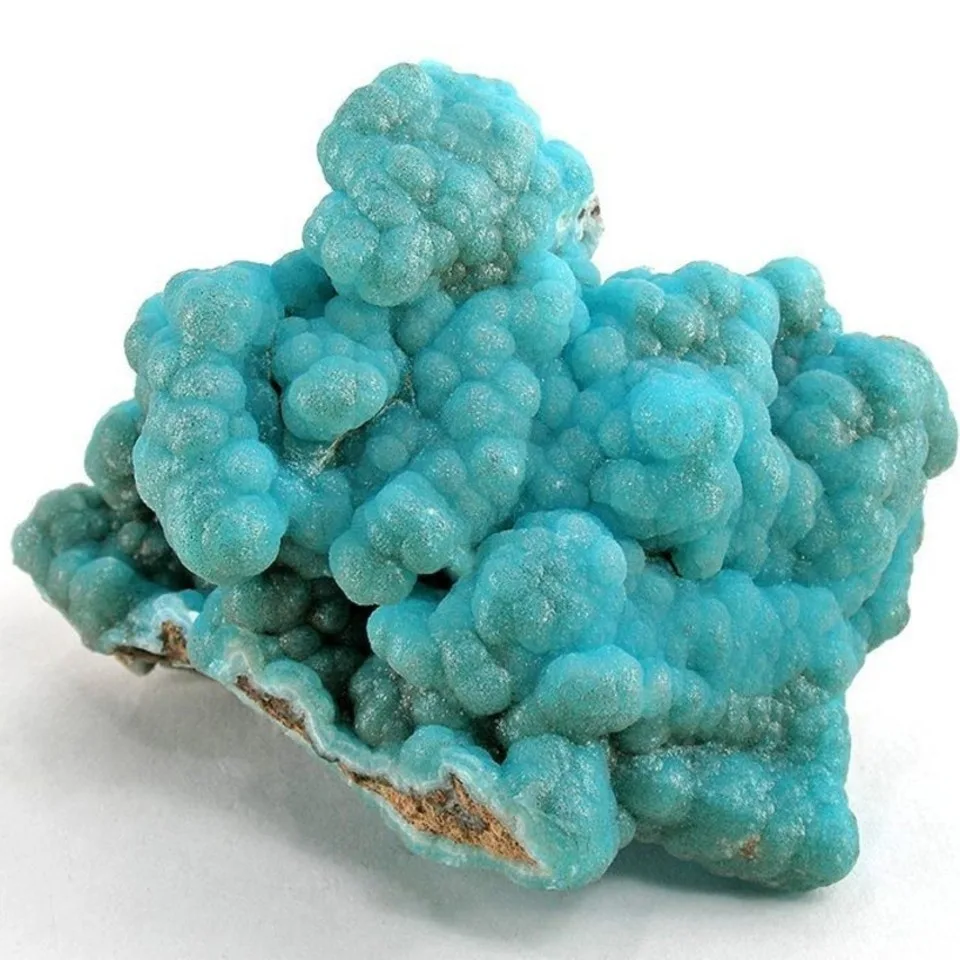
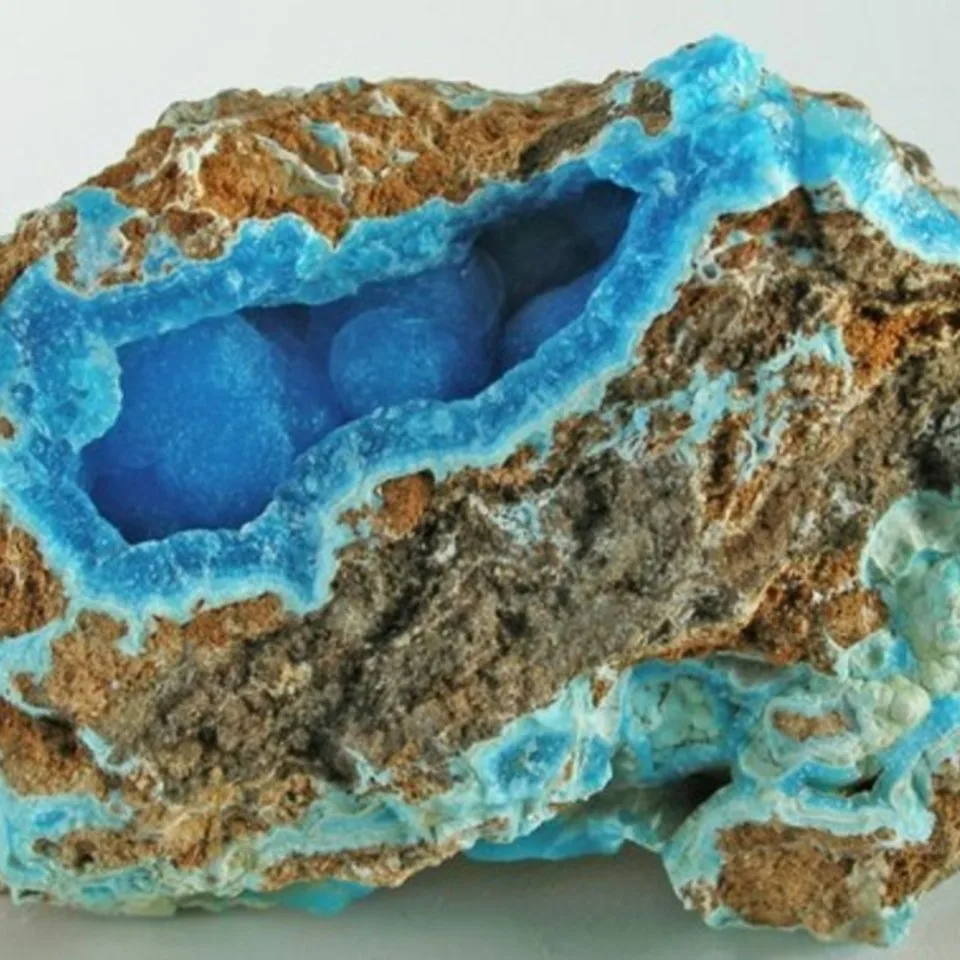
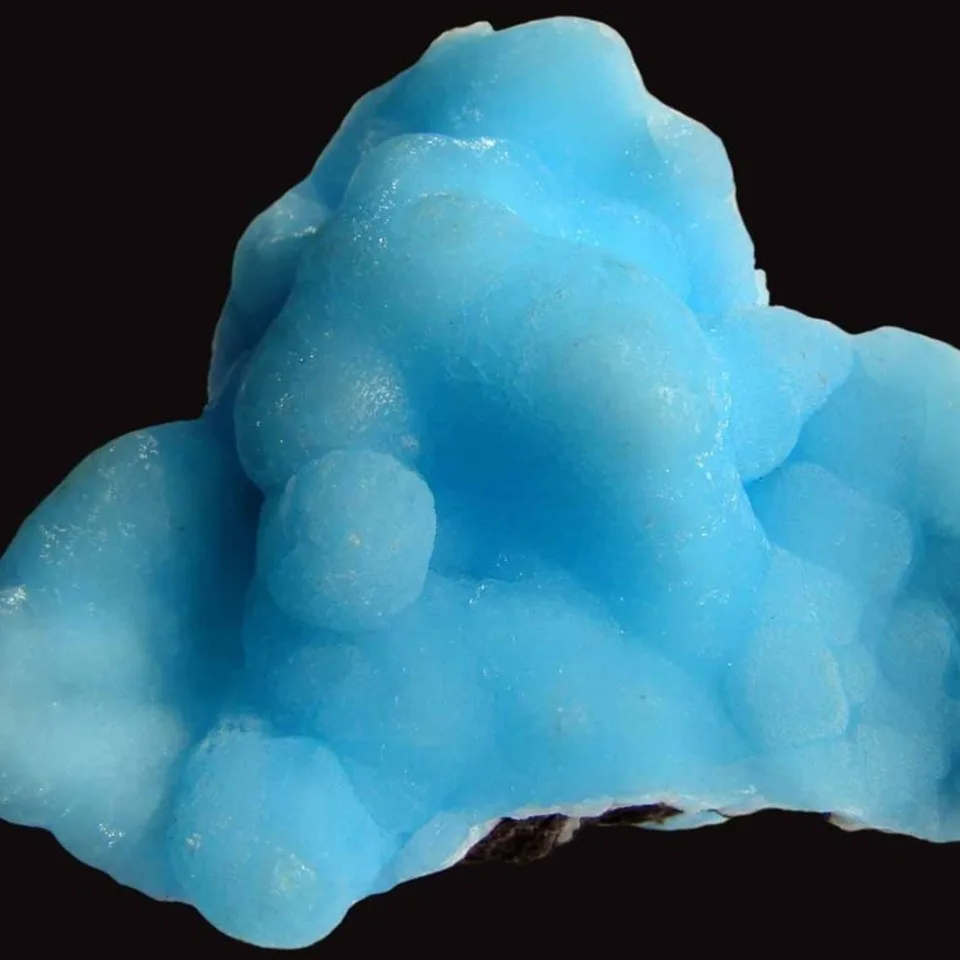
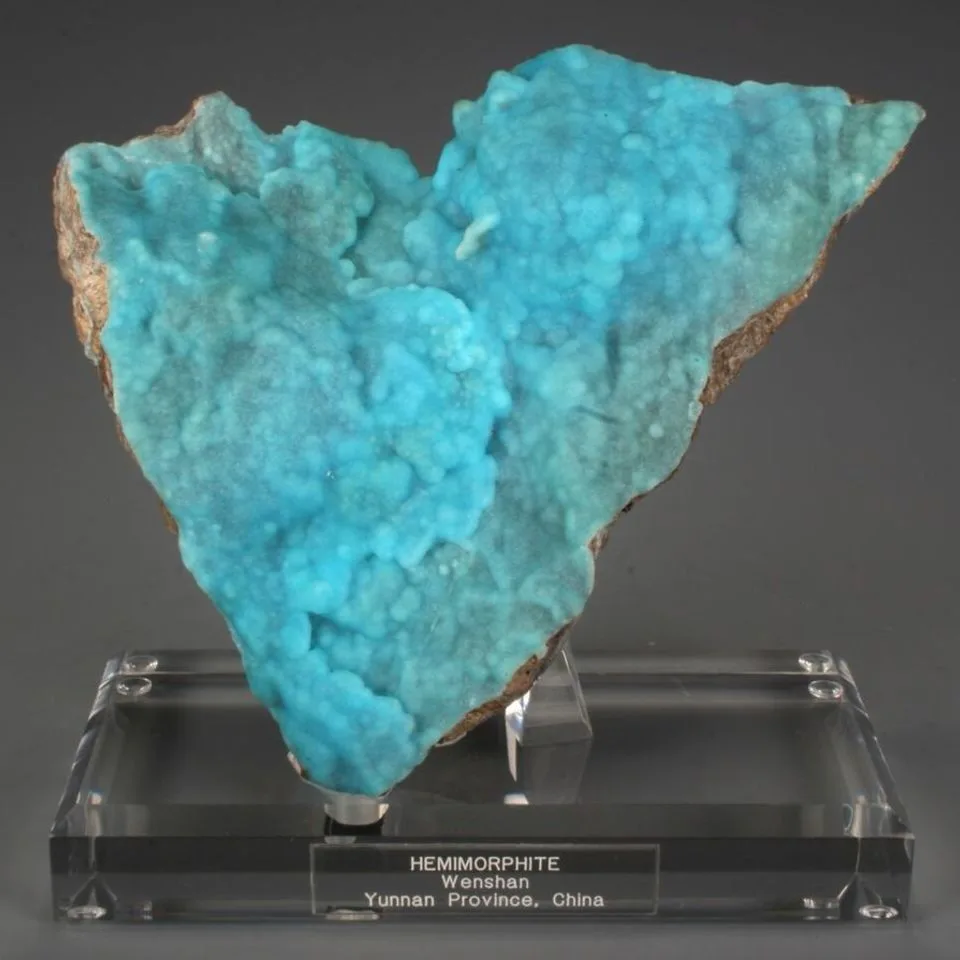
The silicate version was the more rare of the two, and was named hemimorphite because of the hemimorph development of its crystals. This unusual form, which is typical of only a few minerals, means that the crystals are terminated by dissimilar faces. Hemimorphite most commonly forms crystalline crusts and layers, also massive, granular, rounded aggregates, fine needle-shaped, fibrous, or rarely fan-shaped clusters of crystals.
Some specimens show strong green fluorescence in shortwave ultraviolet light and weak light pink fluorescence in longwave UV. Hemimorphite most frequently occurs as the product of the oxidation of the upper parts of sphalerite bearing ore bodies, accompanied by other secondary minerals which form the so-called iron cap or gossan. Hemimorphite is an important ore of zinc and contains more than 50% of the metal. The regions on the Belgian-German border are well known for their deposits of hemimorphite of metasomatic origin, especially Vieille Montagne in Belgium and Aachen in Germany.
Other deposits are near Tarnovice in upper Silesia, Poland; near Phoenixville, Pennsylvania; the Missouri lead-zinc district; Elkhorn, Montana; Leadville, Colorado; and Organ Mountains, New Mexico in the United States; and in several localities in North Africa. Further hemimorphite occurrences are the Padaeng deposit near Mae Sod in western Thailand; Sardinia; Nerchinsk, Siberia; Cave del Predil, Italy; Bleiberg, Carinthia, Austria; Matlock, Derbyshire, England.