Introduction
The Mercenaria permagna, a large quahog clam, is an intriguing species native to the coastal waters of Florida. Known for its substantial size and historical significance, this clam species offers a fascinating glimpse into marine life and the environmental conditions of its habitat. This article delves into the various aspects of the Mercenaria permagna, including its habitat, methods of discovery, formation processes, and its ecological and cultural significance.
Habitat and Distribution
Coastal Waters of Florida
Mercenaria permagna clams are primarily found along the eastern coast of the United States, with a significant population residing in the coastal waters of Florida. These clams thrive in estuarine environments where freshwater from rivers mixes with the saline waters of the ocean. The brackish water conditions, coupled with sandy or muddy substrates, provide an ideal habitat for these bivalves.
Specific Locations
In Florida, the clams are commonly found in areas such as the Indian River Lagoon, Tampa Bay, and the Gulf Coast. These regions offer the right combination of water salinity, temperature, and sediment composition that support the growth and proliferation of Mercenaria permagna. The clams are typically buried a few inches beneath the sediment, making them a bit challenging to locate without proper techniques.

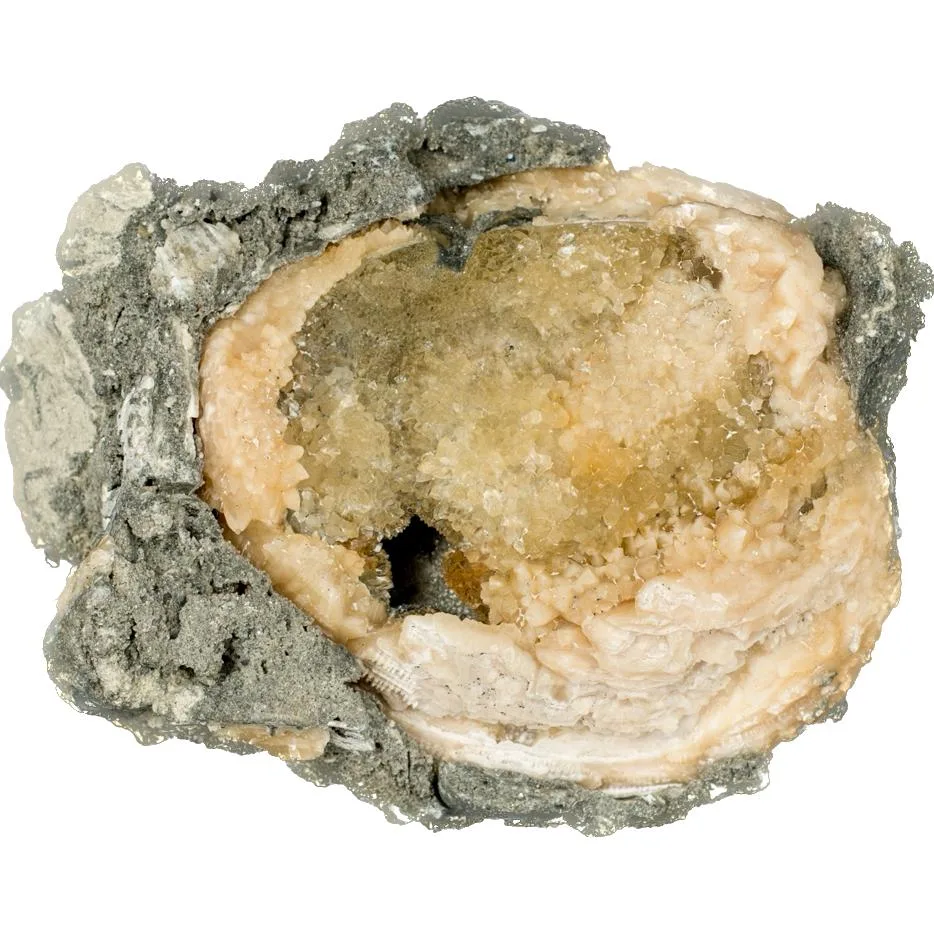
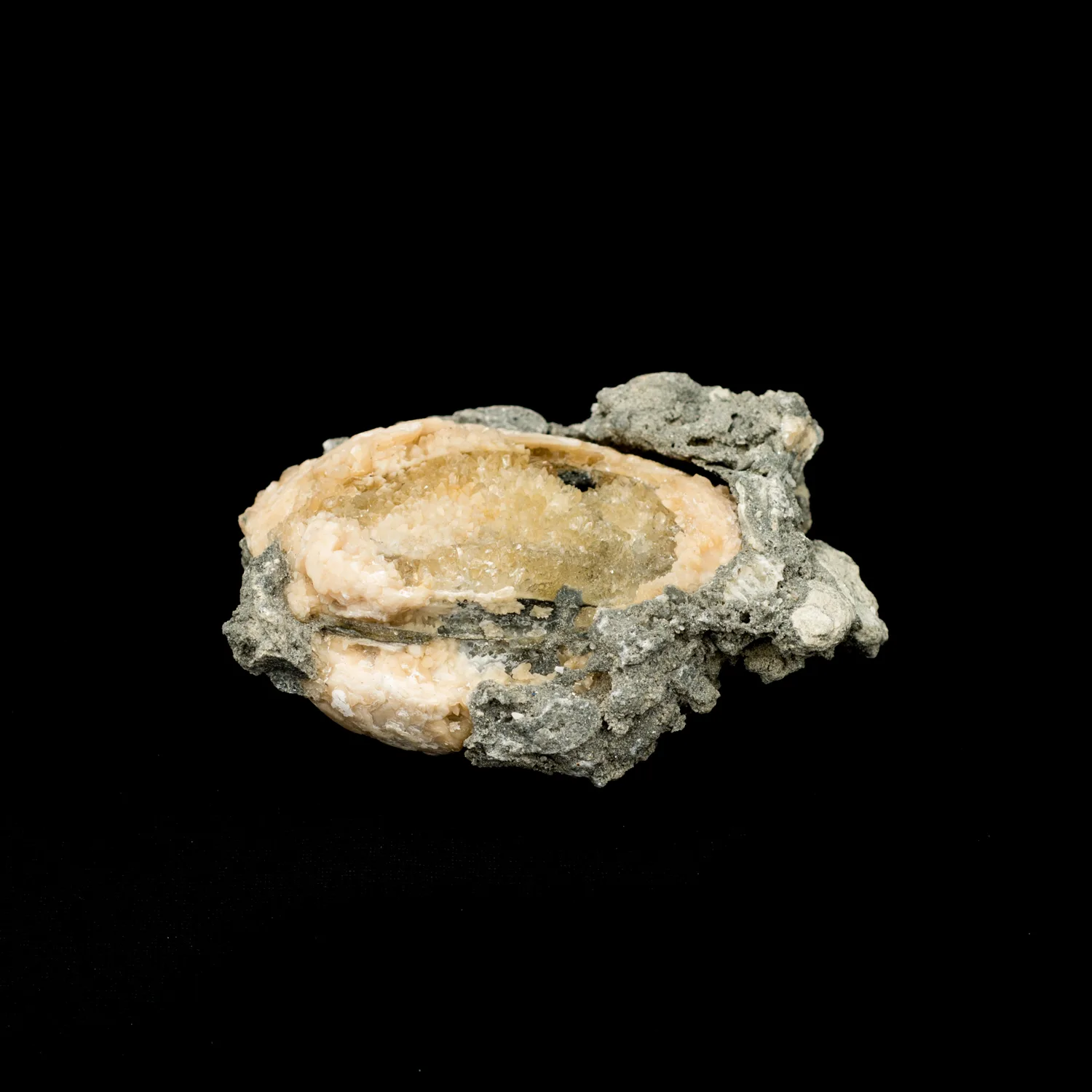
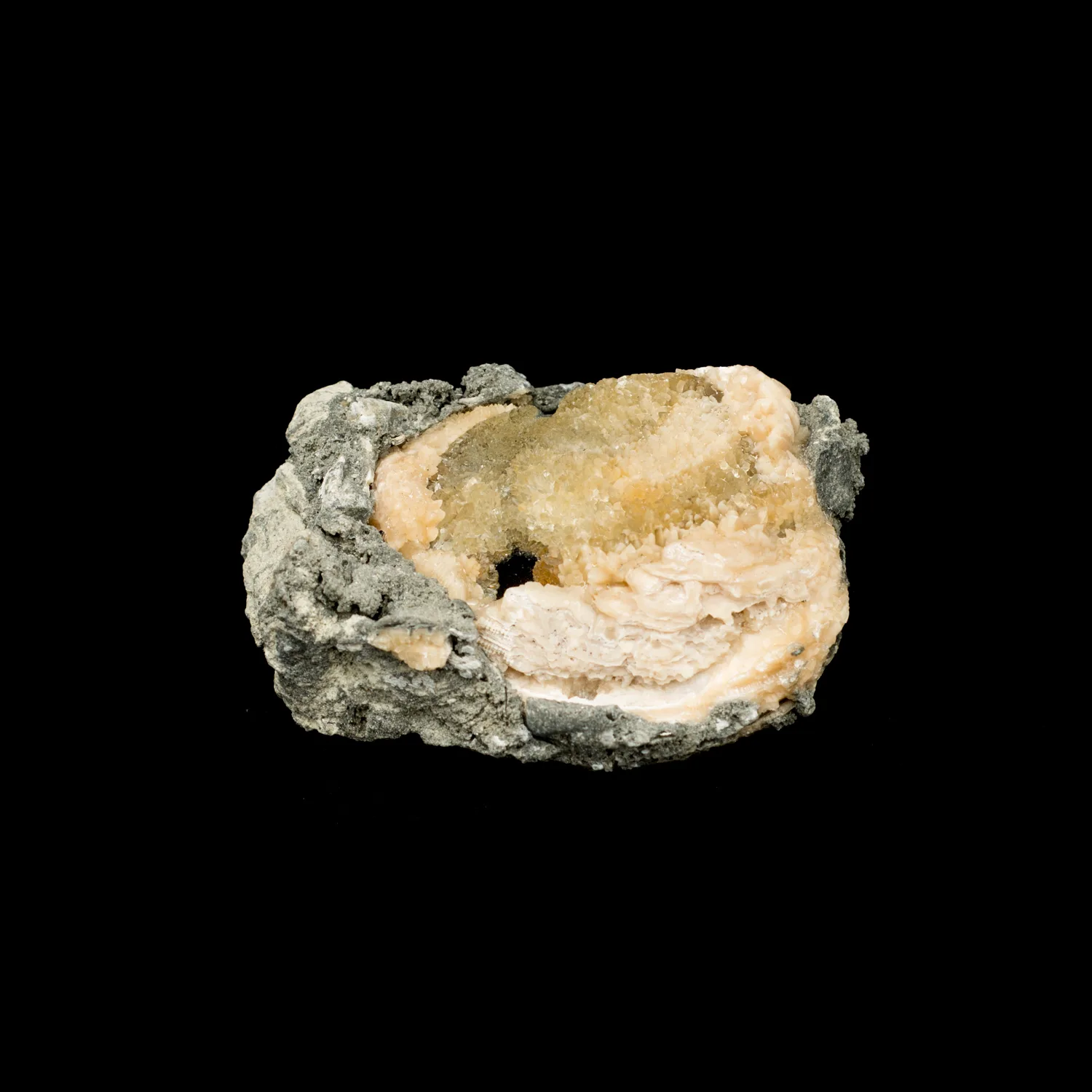
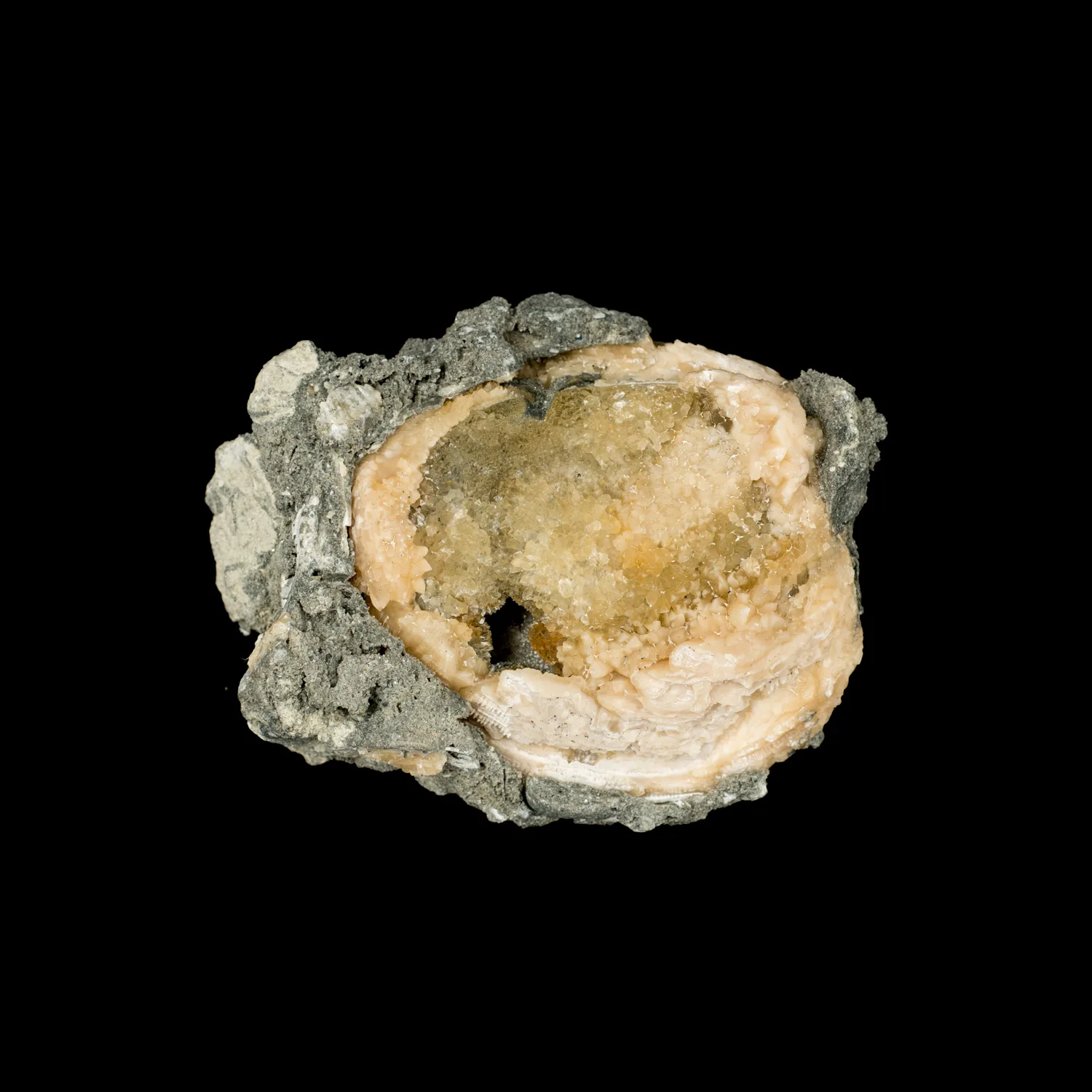
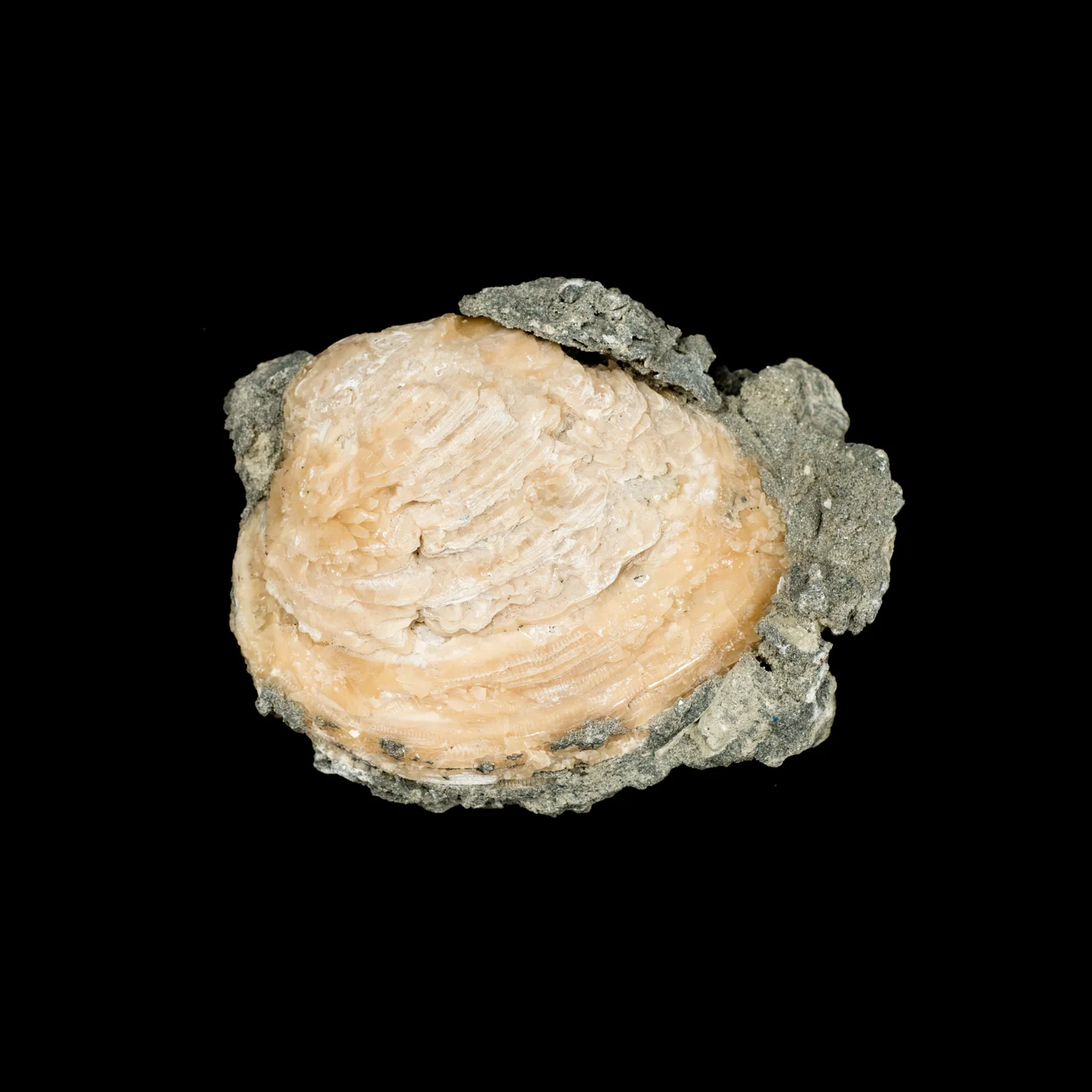
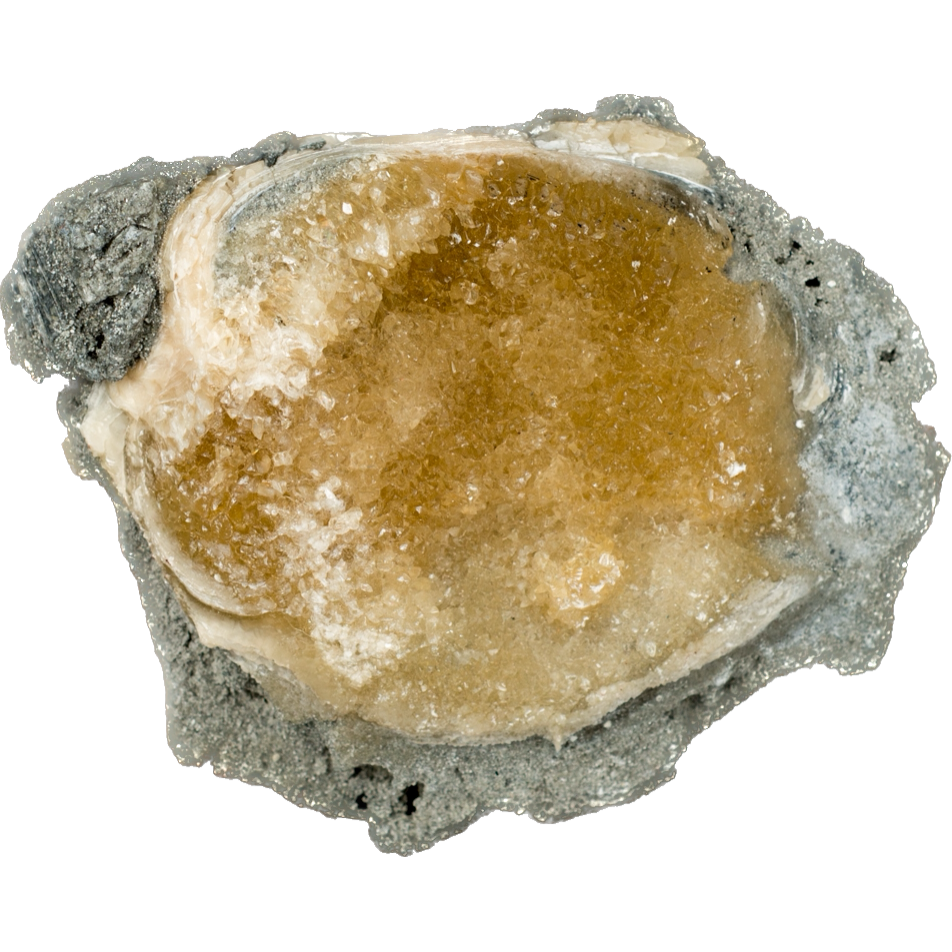
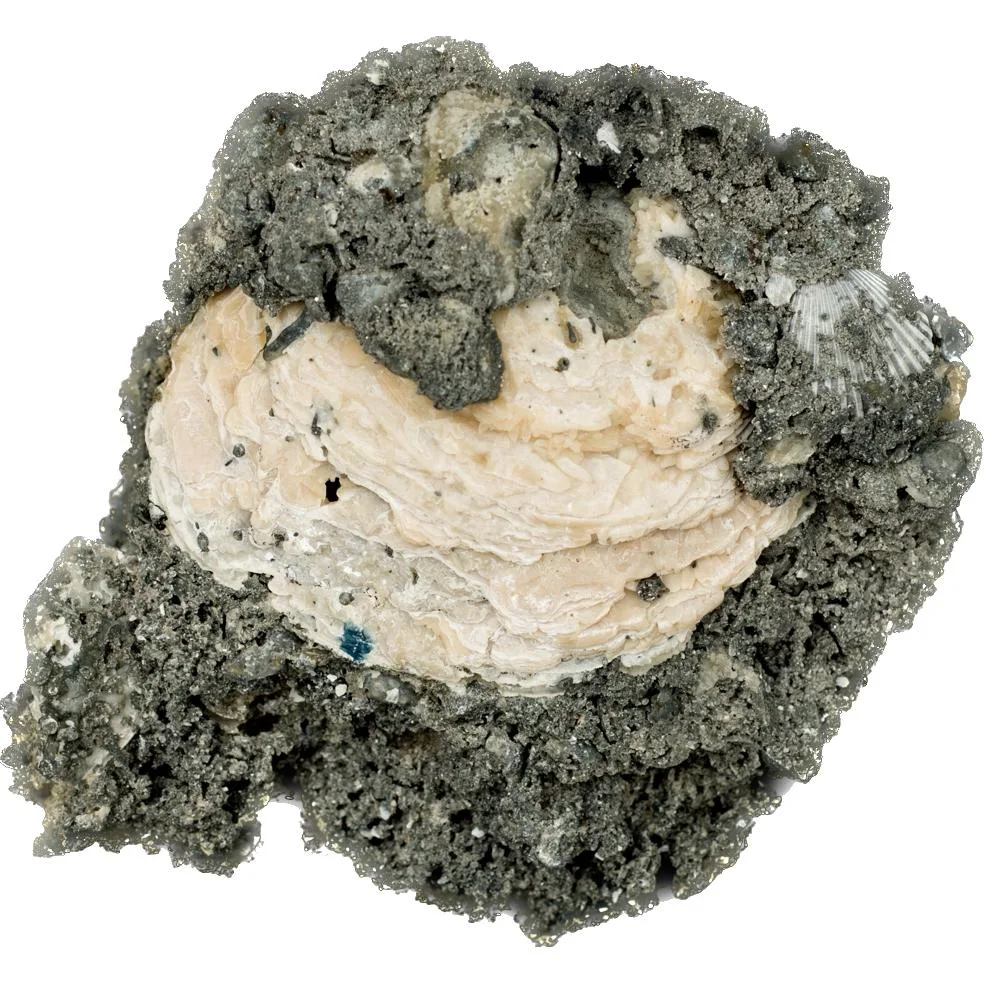
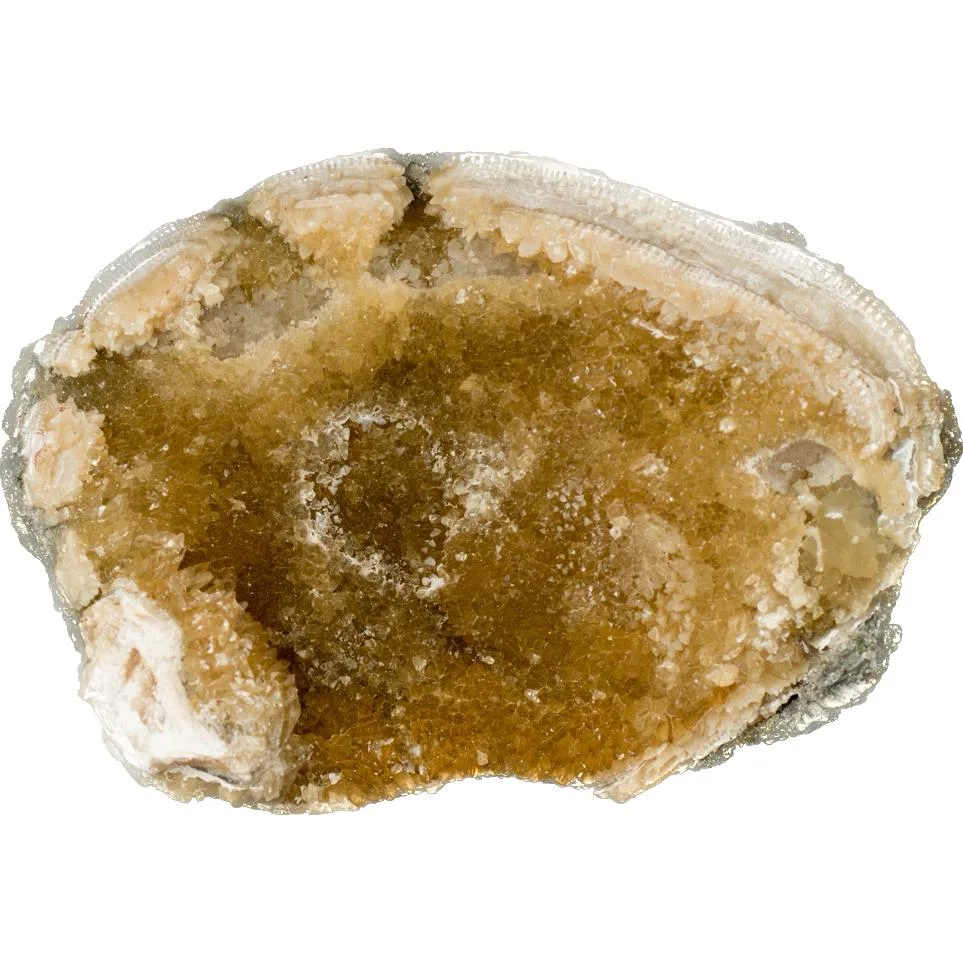
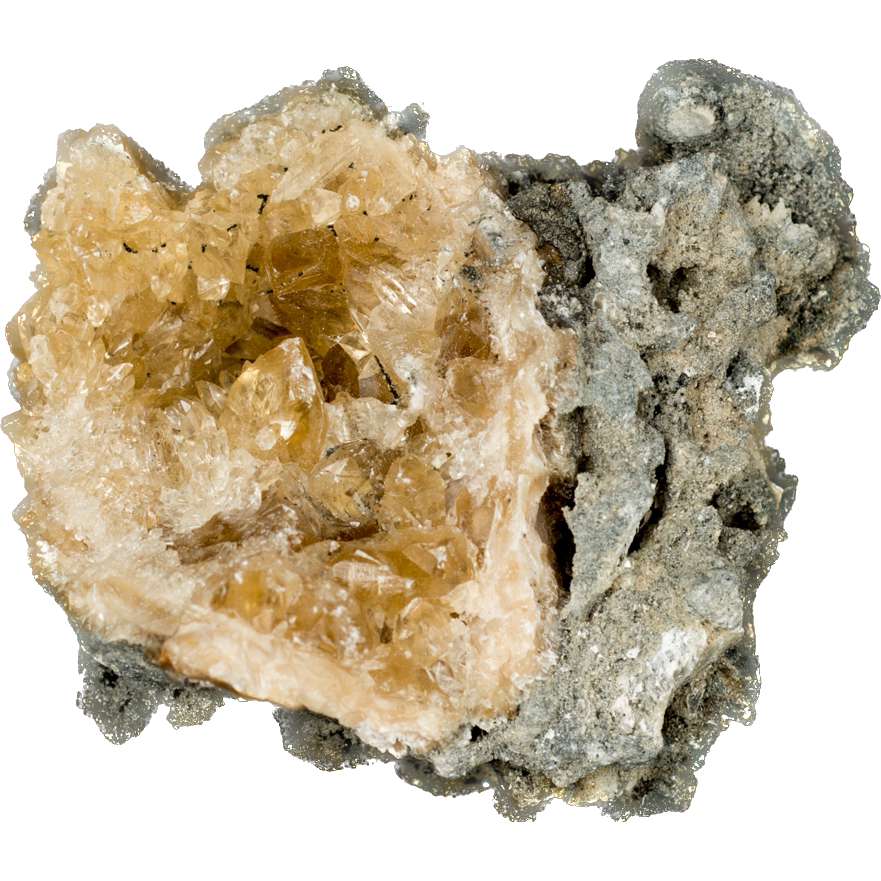
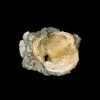
Geodized Mercenaria permagna (fossil bivalve shell) with calcite (Nashua Formation, Lower Pleistocene; near Okeechobee, Florida, USA) by James St. John
Methods of Discovery
Traditional Harvesting Techniques
Historically, indigenous peoples and early settlers in Florida utilized simple tools and manual methods to harvest these clams. Traditional techniques involved feeling the sand with their hands or using small rakes to uncover the clams. This method, though labor-intensive, was effective in gathering clams for food and trade.
Modern Techniques
With advancements in technology, modern methods of discovering and harvesting Mercenaria permagna have evolved significantly. Commercial clam harvesters now use hydraulic dredges and mechanical rakes to collect clams more efficiently. These tools can cover larger areas and dig deeper into the sediment, increasing the yield of clams.
Diving and Snorkeling
Another method used to find these clams involves diving and snorkeling. This technique allows for a more selective and less disruptive approach to harvesting, as divers can identify and collect mature clams while leaving younger ones to grow. This method is particularly popular among recreational clam diggers and researchers studying the species.
Formation and Growth
Larval Stage
The life cycle of Mercenaria permagna begins with the release of larvae into the water column. These larvae are free-swimming and undergo several stages of development before settling onto the substrate. During this period, they are highly vulnerable to predation and environmental factors, which can significantly impact their survival rates.
Settlement and Growth
Once the larvae settle on the substrate, they undergo metamorphosis and begin to grow into juvenile clams. The growth rate of Mercenaria permagna is influenced by various factors, including water temperature, salinity, and availability of food sources such as plankton. The clams secrete calcium carbonate to form their shells, which grow in concentric layers over time.
Adult Stage
As Mercenaria permagna clams reach maturity, they continue to grow, albeit at a slower rate. The size of adult clams can vary, but they are generally known for their substantial size compared to other clam species. The robust shell of Mercenaria permagna provides protection against predators and environmental stresses, contributing to their longevity.
Ecological Significance
Role in the Ecosystem
Mercenaria permagna clams play a crucial role in their ecosystem. As filter feeders, they help maintain water quality by filtering out plankton and other particles from the water column. This process not only provides them with nourishment but also enhances water clarity and quality, benefiting other marine organisms.
Habitat for Other Species
The presence of Mercenaria permagna clams also contributes to the biodiversity of their habitat. Their burrowing activity aerates the sediment, which promotes the growth of seagrass and other benthic organisms. Additionally, their shells provide a hard substrate for various epibionts, such as barnacles and algae, further enriching the ecosystem.
Cultural and Economic Importance
Historical Significance
Mercenaria permagna clams have been an important food source for indigenous peoples and early settlers in Florida. The clams were harvested for their meat, which is rich in protein and other nutrients. The shells were also used in various cultural practices, including tool-making and as a form of currency in some Native American tribes.
Economic Value
Today, Mercenaria permagna clams continue to hold economic value, particularly in the seafood industry. The clams are harvested and sold in markets, where they are prized for their size and flavor. Additionally, the shells are collected and used in various crafts and decorative items, adding to their economic significance.
Conservation and Management
Threats to the Population
Despite their importance, Mercenaria permagna clams face several threats that can impact their populations. Overharvesting, habitat destruction, and pollution are significant concerns. Climate change, with its associated impacts on water temperature and salinity, also poses a risk to the survival of these clams.
Conservation Efforts
To address these threats, various conservation and management strategies have been implemented. These include the establishment of protected areas, restrictions on harvesting during certain periods, and efforts to restore and preserve estuarine habitats. Research and monitoring programs are also in place to track the health and population dynamics of Mercenaria permagna.

Sustainable Harvesting Practices
Promoting sustainable harvesting practices is crucial to ensuring the long-term survival of Mercenaria permagna clams. This involves setting limits on the number of clams that can be harvested, implementing size restrictions to protect juvenile clams, and encouraging the use of less invasive harvesting methods.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing Studies
Research on Mercenaria permagna continues to provide valuable insights into their biology, ecology, and response to environmental changes. Studies focus on various aspects, including growth rates, reproductive biology, and the impacts of pollutants and climate change on their populations.
Future Research Areas
Future research aims to further understand the adaptive mechanisms of Mercenaria permagna in the face of changing environmental conditions. This includes investigating their genetic diversity, potential for acclimatization, and the development of restoration techniques to enhance their populations in degraded habitats.
Climate Change Impacts
Climate change poses a significant threat to the Mercenaria permagna population. Rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and changes in salinity due to altered precipitation patterns can adversely affect their growth and survival rates. Warmer waters may accelerate metabolic rates, leading to increased energy demands and potentially reducing the clams’ ability to reproduce. Ocean acidification, resulting from increased CO2 levels, can weaken their calcium carbonate shells, making them more susceptible to predation and environmental stresses. Understanding and mitigating the impacts of climate change on Mercenaria permagna is crucial for their conservation.
Restoration Efforts
Efforts to restore Mercenaria permagna populations are gaining momentum. Restoration projects often involve the transplantation of juvenile clams into protected areas where they can grow without the pressures of overharvesting and habitat degradation. These initiatives are sometimes supported by hatcheries that cultivate young clams in controlled environments before releasing them into the wild. Additionally, community-based conservation programs engage local stakeholders, including fishermen and coastal residents, in monitoring and protecting clam habitats. These collaborative efforts are essential for the successful recovery and sustainability of Mercenaria permagna populations.
Educational and Ecotourism Opportunities
Mercenaria permagna clams also offer opportunities for education and ecotourism. Coastal regions in Florida can develop educational programs and ecotourism activities that highlight the ecological and cultural importance of these clams. Guided tours, interactive exhibits at marine centers, and school programs can raise awareness about the species and the challenges they face. By fostering a deeper connection between the public and the natural environment, these initiatives can promote conservation efforts and sustainable practices. Ecotourism, in particular, can provide economic benefits to local communities while encouraging the protection of vital marine habitats.
Prehistoric 101 (Learn about fossils, minerals, and meteorites)
Unearthing History: The Fascinating World of Mercenaria Permagna Clams from Florida